Regions
Regions are a type of filter that filters the coordinates of a query.
They are used to define, among other things, the area a filter applies to or where a portal links from.
There are two distinct types of regions; block bounded regions,
which contain a finite amount of blocks and unbounded regions that contain a infinite amount.
All regions and region modifiers can have a id attribute to reference them from kits, portals, etc.
<regions>
<rectangle id="xyzzy-region" min="-50,-50" max="50,50"/>
</regions>
<!-- Region reference -->
<region id="xyzzy-region"/>
The area a region applies to is specified with one or more of the following elements.
Use oo and -oo to specify positive/negative infinity in coordinates.
See the Properly Defining Regions guide for information on how to properly get the coordinates of a region.
Region Types
Block Bounded Regions
| Block Bounded Regions | |
|---|---|
<cuboid id="abc" min="X1,Y1,Z1" max="X2,Y2,Z2"/><cuboid min="X1,Y1,Z1", size="30,10,40"/><cuboid max="X2,Y2,Z2", size="30,10,40"/>A rectangular solid from X1,Y1,Z1 to X2,Y2,Z2.Using the size attribute offsets the original min/max value by size. ie. (min + size = max) & (max - size = min)Only block bounded when using finite coordinates. | Randomize-able |
<cylinder id="abc" base="X,Y,Z" radius="R" height="H"/>A cylinder located at X,Y,Z with a radius of R and a height of H.Only block bounded when using a finite radius. | Randomize-able |
<block id="abc">X,Y,Z</block>A single block located at X,Y,Z. | Randomize-able |
<sphere id="abc" origin="X,Y,Z" radius="R"/>A sphere located at X,Y,Z with a radius of R.Only block bounded when using a finite radius. | Randomize-able |
<point id="abc">X,Y,Z</point>A single point region located at X,Y,Z.This region will always return the same location even when used in a randomized context, e.g., spawns. | Randomize-able |
Unbounded Regions
| Unbounded Regions |
|---|
<rectangle id="abc" min="X1,Z1" max="X2,Z2"/>A rectangle from X1,Z1 to X2,Z2. |
<circle id="abc" center="X,Z" radius="R"/>A circle located at X,Z with a radius of R.The region goes from 0 to map height, i.e. PGM doesn't check the players Y position. |
<half normal="1,0,1" origin="100,50,0" id="abc"/>Half of the world split by a plane pointing towards a normal. |
<below x="" y="" z="" id="abc"/><above x="" y="" z="" id="abc"/>Half of the world split at the specified axis. If multiple axises are defined, the specified parts of each axis are intersected and returned. |
Static Regions
| Static Regions |
|---|
<empty/>A zero size/position region, contains nothing. |
<nowhere/>A reference-able zero size/position region, contains nothing. Can be referenced with the region ID: nowhere. |
<everywhere/>A reference-able infinite size region, contains everything. Can be referenced with the region ID: everywhere. |
Half-space Regions
A half-space region contains everything on one side of an arbitrary plane. The plane is defined by an origin point and a normal vector, and the region contains everything on the side of the plane that the normal is pointing towards. The example below defines a region with a diagonal boundary:
<half origin="5,0,0" normal="1,1,0"/>
The above and below regions can be used to conveniently define axis-aligned half-spaces:
<above y="50"/> <!-- Everything above Y=50 -->
<below x="0" z="0"/> <!-- Everything in the -X, -Z quadrant -->
Applying Things to Regions
Filters, kits, and velocity changes can be applied to regions by using an <apply> element.
The apply element can contain more than one region.
If the apply element contains more than one region the same settings are applied to all of them.
Applies with no region default to <everywhere/>. Applies can also be defined in the filters element.
The order in which apply elements are specified determines which takes precedence when regions overlap.
Applies specified first override those specified further down in the XML.
See Filter Apply Order for a more detailed example.
The region an apply affects can be specified as an attribute or in a <region> sub-element.
Apply Element Attributes
| Attribute | Description | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
region | PropertyThe region this apply affects. | Region | |
enter | PropertyFilter player enter events. | Filter | |
leave | PropertyFilter player leave events. | Filter | |
block | PropertyFilter block place and break events. | Filter | |
block-place | PropertyFilter block place events. | Filter | |
block-place-against | PropertyFilter block place against events. | Filter | |
block-break | PropertyFilter block break events. | Filter | |
block-physics | PropertyFilter world block updates; water flowing, portals disappearing, etc. | Filter | |
use | PropertyFilter right-click events. | Filter | |
message | Send a message to the player if the filter denies the event. | String | |
early-warning | Warn the player before they actually break a denied block. | String | false |
Apply Effects
| Attribute | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
kit | PropertyGive a kit to players entering the region. | Kit |
lend-kit | PropertyGive a kit to players entering the region, and remove it when they leave the region. This can be used only with removable kits. Any non-removable kit will generate an error. The kits page explains which kit types are removable. | Kit |
velocity | Change a player's velocity when they enter the region. | X,Y,Z |
filter | PropertyFilter when/if kits and velocities are applied. | Filter |
Apply Examples
<!-- Apply a blue team usage filter and referenced the region in an attribute. -->
<apply region="region1" use="blue-team-filter"/>
<apply kit="dark-tower-kit">
<region>
<!-- Multiple regions or region references in a regions sub-element. -->
<region id="region1"/>
<rectangle min="-5,-5" max="5,5"/>
</region>
<!-- Inline effect filter -->
<filter>
<team>blue</team>
</filter>
</apply>
Examples
<!-- Give a kit to players entering the region. -->
<apply kit="knight">
<region>
<region id="r-knight"/>
<region id="b-knight"/>
</region>
</apply>
<!-- Only allow breaking of sandstone stairs and deny placing of all blocks. -->
<apply block-break="only-sandstone-stairs" block-place="never" message="You may not modify this area">
<region>
<rectangle min="-6,-58" max="7,-47"/>
<rectangle min="-6,48" max="7,59"/>
</region>
</apply>
<!-- Example regions from Harb using region modifiers. -->
<regions>
<rectangle id="main-area" min="-50,-32" max="51,33"/>
<union id="bases">
<rectangle id="blue-base" min="-20,-62" max="21,-32"/>
<rectangle id="red-base" min="-20,33" max="21,63"/>
</union>
<complement id="portals-area">
<rectangle min="-56,-2" max="57,3"/>
<region id="main-area"/>
</complement>
<!-- Protect portal areas -->
<apply block="never" region="portals-area"/>
<apply block="no-tnt" region="bases" message="You may not place TNT in the bases."/>
</regions>
Applying Velocities to Regions
An applies velocity attribute changes the players velocity when they enter the specified region.
This velocity is specified as a X,Y,Z vector.
Example using velocity for jump pads
<regions>
<!-- Yellow Pads -->
<apply velocity="-0.4,1.1,0.0">
<region>
<cuboid min="-1081,1,-2116" max="-1078,2,-2113"/>
</region>
</apply>
<apply velocity="0.0,1.4,-0.4">
<region>
<cuboid min="-1062,1,-2123" max="-1059,2,-2120"/>
</region>
</apply>
</regions>
Region Modifiers
Regions can be inverted, combined, subtracted, or intersected by putting them inside of the following elements.
| Region Modifiers |
|---|
<negative><region id="region1"/></negative>Inverse of a region, the region or regions will no longer be considered block bounded. |
<union><region id="region1"/><region id="region2"/>..</union>Combination of multiple regions. |
<complement><region id="region1"/><region id="region2"/>..</complement>Subtracts successive regions from the first defined region. |
<intersect><region id="region1"/><region id="region2"/>..</intersect>Returns the area that multiple regions intersect with. |
Region Combinations Diagram

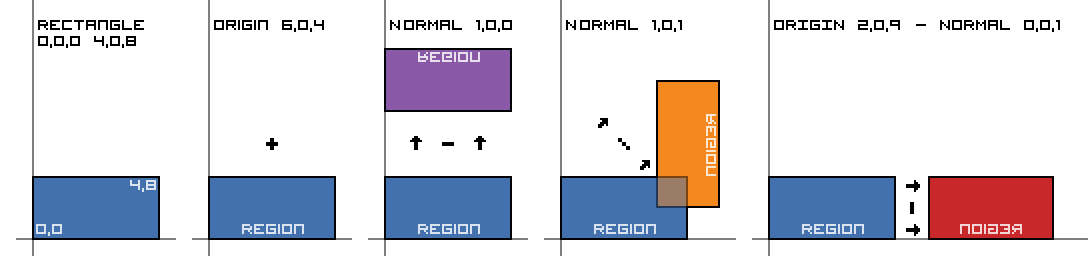
Regions can be translated or mirrored with the following elements. When translating or mirroring a region the original is not modified instead a copy is created.
When mirroring a region the origin is the central point around which the region is mirrored.
This point can be inside or outside the region being mirrored.
The normal specifies which direction the region is being mirrored, e.g., 1,0,0 would mirror along the +X axis.
| Region Transformation |
|---|
<translate offset="X,Y,Z"><region id="region1"/></translate>Copy and translate a region by X,Y,Z blocks. |
<mirror normal="1,0,1" origin="100,50,0"><region id="region1"/></mirror>Copy and mirror a region towards a normal around a point. |
Region Mirrors Diagram
Examples
<!-- Region Union-->
<regions>
<!-- Blue Team Base -->
<apply enter="only-blue" message="You may not enter the enemy team's base!">
<region>
<union>
<cuboid min="-20,8,-75" max="11,41,-79"/>
<cuboid min="8,8,-80" max="13,41,-75"/>
</union>
</region>
</apply>
</regions>
<!-- Region Mirror -->
<regions>
<apply block="never" message="You may not under-bridge!">
<region>
<cuboid id="red-underside" min="-oo,-oo,-oo" max="oo,41,40"/>
<mirror origin="116,44,93" normal="0,0,1">
<region id="red-underside"/>
</mirror>
<below y="37"/>
</region>
</apply>
</regions>
Point Providers
A point provider is used to return individual points inside a region.
It can also be used to modify the position returned by a region to include the direction a player ends up facing when spawned, etc.
Input can be a region, a region modifier or simply an exact X,Y,Z coordinate.
<point yaw="90" pitch="50">X,Y,Z</point>
Copy the yaw and pitch from the Debug screen (F3) in Minecraft (the Facing: Direction (Axis) (Yaw/Pitch) line).
Point Attributes
| Attribute | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
region | PropertyThe region (or regions) the point provider modifies. | Randomize-able Region |
yaw | Specifies what direction the player is looking horizontally from -180° to 180°. South 0°, East -90°, North 180°, and West 90°. | -180 to 180 |
pitch | Specifies what direction the player is looking vertically from -90° to 90°. -90° is straight up, 90° is straight down. | -90 to 90 |
angle | Specify the exact block coordinates that the player should look at. This attribute will negate any angles set by the yaw and pitch attributes. | X,Y,Z |
Note: The pitch and yaw arguments can also accept a X,Y,Z coordinate.